¿Qué es el Carburante sintético o e-Fuel?
El e-Fuel o carburante sintético es un carburante líquido, muy similar al que conocemos en la actualidad. La gran diferencia es que no procede de fuentes de energía fósiles, sino de un proceso químico a partir del hidrógeno, y la energía que se utiliza para su fabricación es renovable, de forma que se trata de un combustible 100% limpio.
Los combustibles sintéticos nacen como una alternativa real a los problemas de limitación en la autonomía de las baterías actuales dada su mayor densidad energética. Si se encuentra un proceso de manufactura que permita desarrollar dichos combustibles sintéticos sin elevados costes, los motores de combustión podrían volverse totalmente neutrales en sus emisiones de carbono.
Hablando en cifras, el resultado neto podría ser una reducción de 2,8 gigatoneladas de CO2 en Europa de cara a 2050. Y lo mejor de todo es que los e-Fuels pueden utilizarse en múltiples aplicaciones.
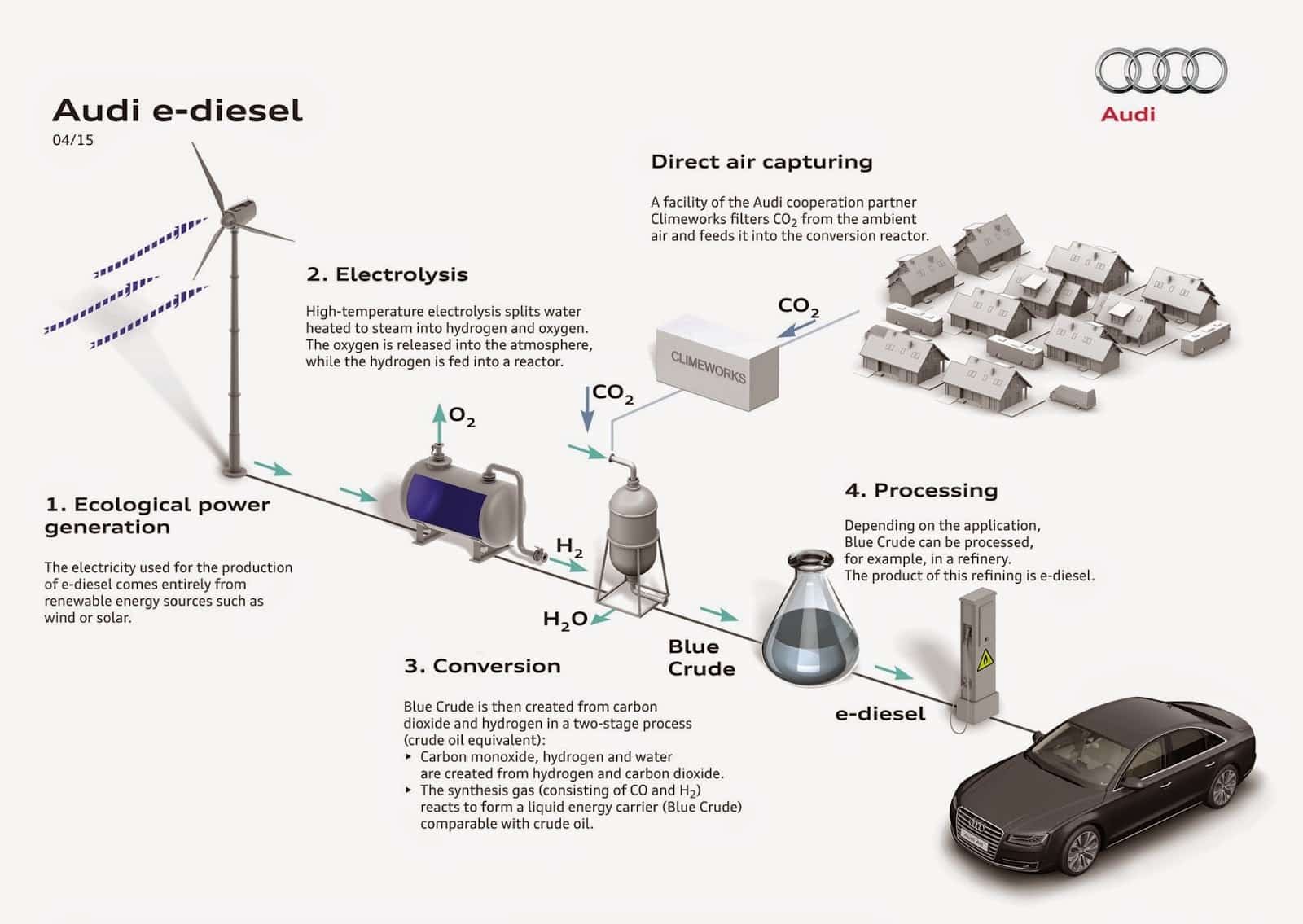
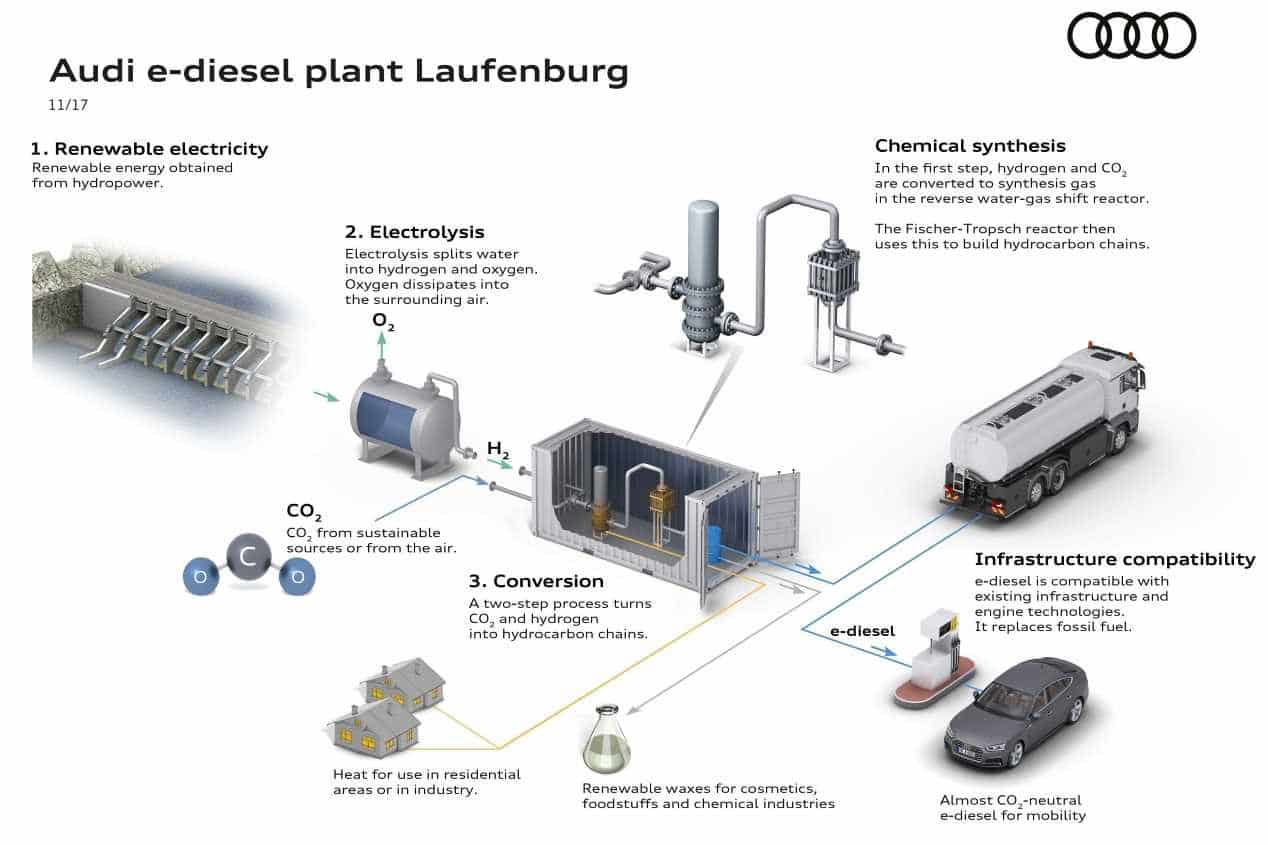
Obtención del combustible sintético
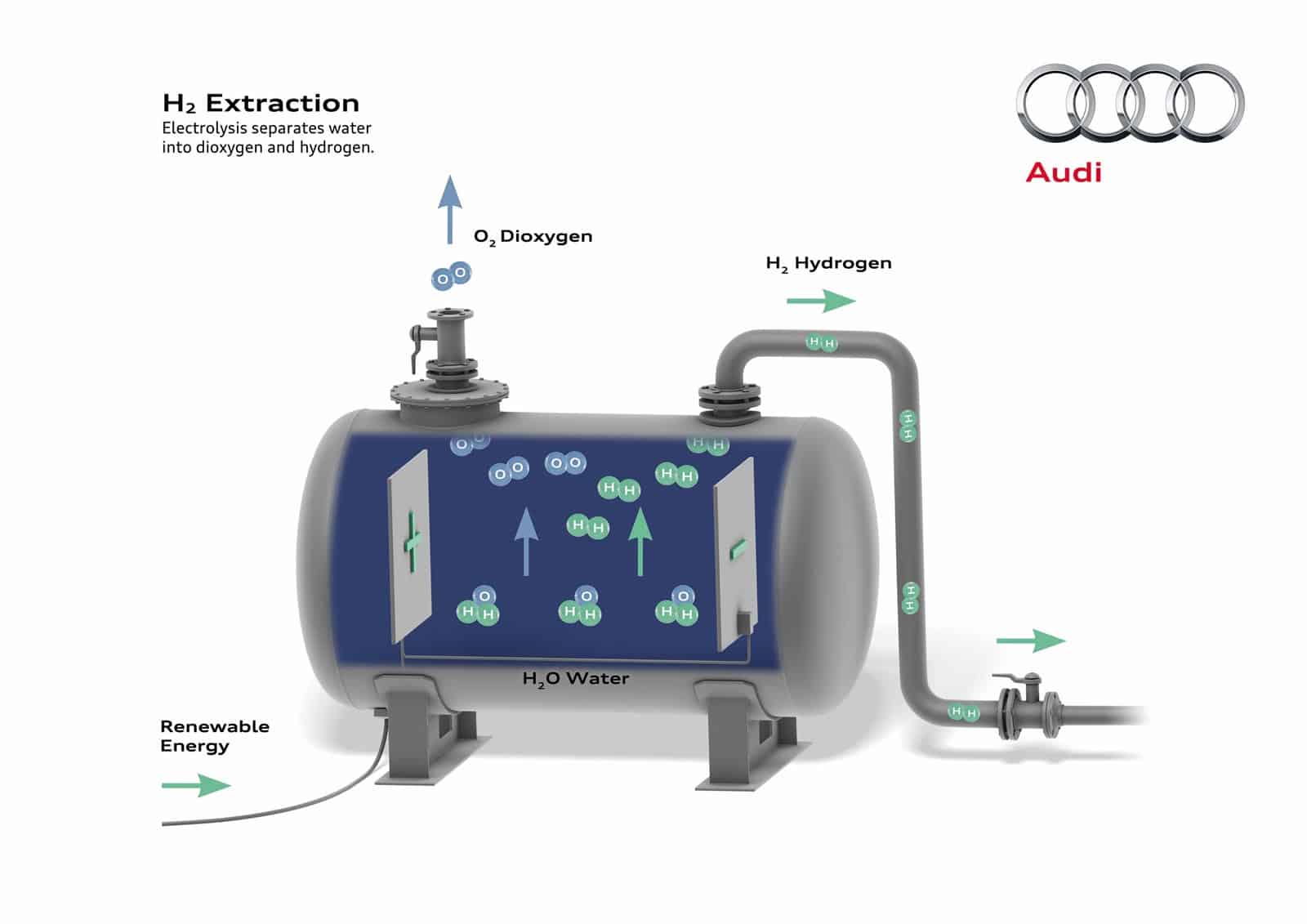
Para el método de fabricación se captura CO2 en lugar de liberarlo. Para crear los e-Fuels, el propio gas de efecto invernadero actúa como materia prima. El primer paso es adquirir hidrógeno del agua, separándoles mediante la técnica de la electrólisis.
Posteriormente, se añade carbón para generar un combustible líquido. Dicho carbón puede obtenerse o bien a través del reciclado del mismo en los procesos industriales o capturándolo del aire gracias a filtros especiales. Cuando combinamos el hidrógeno y el dióxido de carbono (CO2) obtenemos el combustible sintético (metano), que puede ser gasolina, diésel, gas e incluso queroseno.
Adicionalmente, estos combustibles pueden ser diseñados para quemar la mezcla sin generar hollín, lo que reduce los costes de tratamiento de los gases del escape. Y como los combustibles fósiles, se puede transportar y almacenar de manera segura y durante períodos de tiempo prolongados, aprovechando toda la red de distribución y almacenaje actuales.
Futuro de los carburantes sintéticos
Actualmente ya están en marcha algunos proyectos piloto para comercializar diésel sintético, gasolina y gas natural en Noruega y Alemania, aunque desde Bosch han querido dejar claro que hay que hacer esfuerzos considerables antes de que los combustibles sintéticos se establezcan totalmente, pues crear las instalaciones de procesamiento de combustibles sintéticos supone un gran desembolso.
En la actualidad, producir e-Fuel a gran escala es ineficiente porque apenas se aprovecha la mitad de la energía eléctrica que se invierte, y dicha energía debe de ser completamente renovable (hidroeléctrica, energía solar, eólica o nuclear) para que este sea neutro en carbono.
A diferencia de lo que ocurre con los bio-combustibles, si se usan energías renovables para su fabricación, los combustibles sintéticos pueden producirse sin las limitaciones de volumen que se esperan con los bio-combustibles a causa de factores como el espacio disponible para su producción o la deforestación.


